Test
Documentation of the demonstration cases located in test.
Transfinite Mesh interTransMesh
Create a simple geometry by an intersection of two curves and mesh a four sided face with quadrangles.
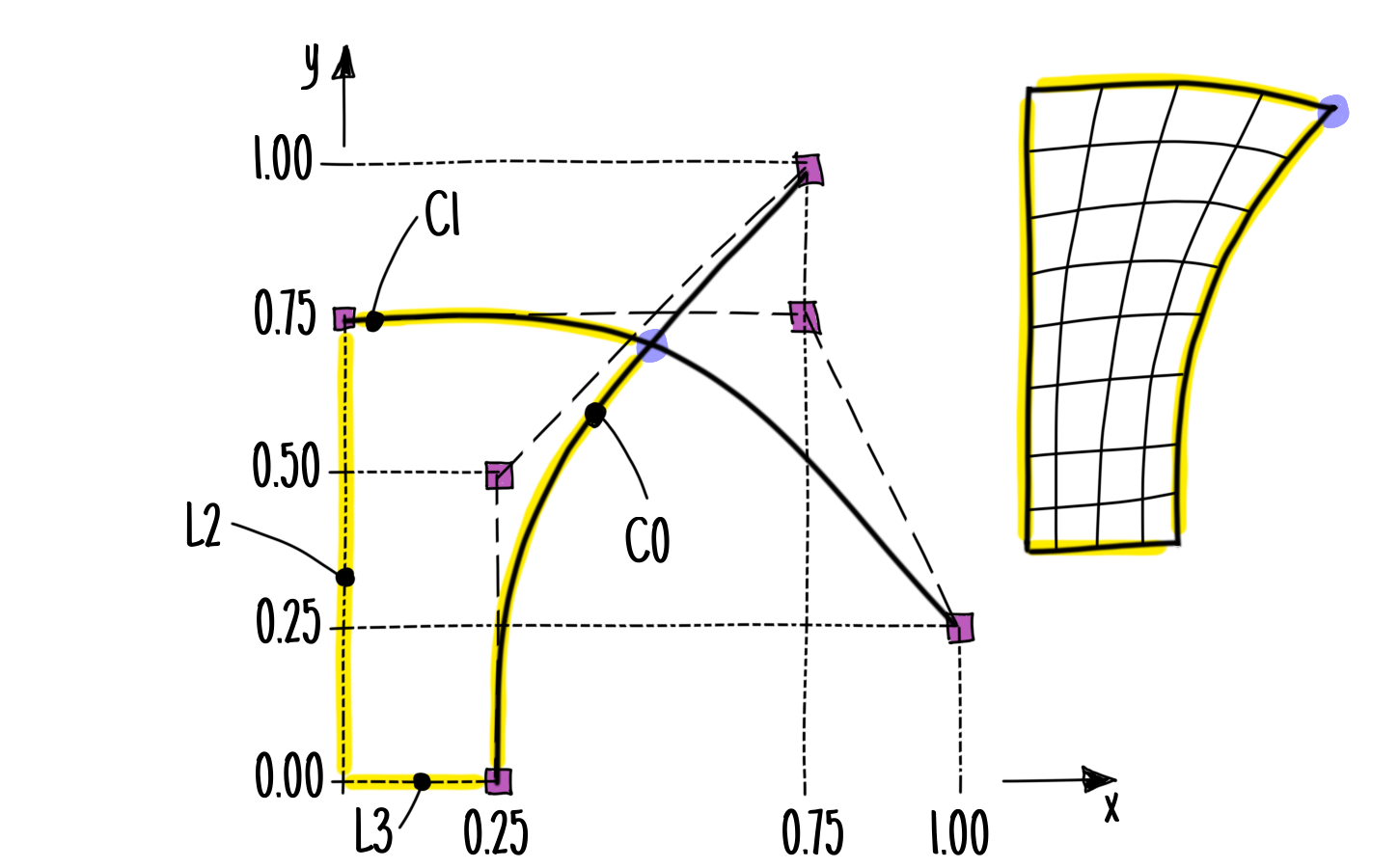
Fig. 9 Sketch of geometry and mesh including control points (magenta colored), B-Splines (black thick solid), intersection point (magenta colored), and mesh face’s boundaries (yellow colored); transfinite mesh shown on the right hand side
Import dtOO:
>>> import dtOOPythonSWIG as dtOO
Define dtOO’s options:
>>> dtOO.staticPropertiesHandler.getInstance().jInit(
... dtOO.jsonPrimitive(
... '{'
... '"option" : ['
... '{"name" : "reparamOnFace_precision", "value" : "1.e-05"},'
... '{"name" : "reparamInVolume_precision","value" : "1.e-05"},'
... '{"name" : "invY_precision", "value" : "1.e-04"},'
... '{"name" : "xyz_resolution", "value" : "1.e-05"},'
... '{"name" : "XYZ_resolution", "value" : "1.e-04"},'
... '{"name" : "uvw_resolution", "value" : "1.e-04"},'
... '{"name" : "point_render_diameter", "value" : "0.005"},'
... '{"name" : "vector_render_size", "value" : "0.05"},'
... '{"name" : "function_render_resolution_u", "value" : "21"},'
... '{"name" : "function_render_resolution_v", "value" : "21"},'
... '{"name" : "function_render_resolution_w", "value" : "21"},'
... '{"name" : "geometry_render_resolution_u", "value" : "21"},'
... '{"name" : "geometry_render_resolution_v", "value" : "21"},'
... '{"name" : "geometry_render_resolution_w", "value" : "21"},'
... '{"name" : "ompNumThreads", "value" : "2"},'
... '{"name" : "map1dTo3d_deltaPer", "value" : "0.01"},'
... '{"name" : "map2dTo3d_deltaPer", "value" : "0.01"},'
... '{"name" : "map3dTo3d_deltaPer", "value" : "0.01"},'
... '{"name" : "logLevel", "value" : "0"},'
... '{"name" : "isEqualExtendCheck", "value" : "false"}'
... ']'
... '}'
... )
... )
Create a log file:
>>> dtOO.logMe.initLog('interTransMesh.log')
'interTransMesh.log'
Create a dtBundle object; this is necessary for the definition of a
labeledVectorHandlingConstValue object that is observed by a
dtOO.lVHOstateHandler.clear:
>>> container = dtOO.dtBundle()
>>> cV = container.cptr_cV()
>>> dtOO.lVHOstateHandler.clear()
>>> dtOO.lVHOstateHandler( dtOO.jsonPrimitive(), cV).thisown = False
Create a B-Spline curve with three control points and of second order; the
__lshift__- or <<-operator appends the points to the
vectorDtPoint3 object:
>>> C0 = dtOO.bSplineCurve_pointConstructOCC(
... dtOO.vectorDtPoint3()
... << dtOO.dtPoint3(0.25,0.00,0.00)
... << dtOO.dtPoint3(0.25,0.50,0.00)
... << dtOO.dtPoint3(0.75,1.00,0.00),
... 2
... ).result()
Create a second B-Spline curve:
>>> C1 = dtOO.bSplineCurve_pointConstructOCC(
... dtOO.vectorDtPoint3()
... << dtOO.dtPoint3(0.00,0.75,0.00)
... << dtOO.dtPoint3(0.75,0.75,0.00)
... << dtOO.dtPoint3(1.00,0.25,0.00),
... 2
... ).result()
Create a minimization object to find the intersection point of two curves; the
object is created with a subclass of floatAtt; different choices are
implemented in attributionHeaven;
the class curveCurveDist calculates the distance of two points that are
on two different curves:
>>> gmf = dtOO.gslMinFloatAttr(
... dtOO.curveCurveDist(C0,C1),
... dtOO.vectorReal([0.5, 0.5,]),
... dtOO.vectorReal([0.001, 0.001,]),
... 1.e-8,
... 100
... )
Perform the minimization; the result is stored in an internal vector that can
be accessed via the result() function:
>>> gmf.perform()
True
Create the B-Spline surface; the builder
bSplineSurface_bSplineCurveFillConstructOCC takes four curves as input
and constructs a B-Spline surface; the boundary curves are constructed as
straight line (L3 and L2 in Fig. 9) or trimmed curve
(pieces of C0 and C1 in Fig. 9):
>>> S0 = dtOO.bSplineSurface_bSplineCurveFillConstructOCC(
... dtOO.bSplineCurve_pointConstructOCC(
... dtOO.dtPoint3(0,0,0), C0.pointPercent(0.0)
... ).result(),
... dtOO.trimmedCurve_uBounds(
... C0, 0.0, C0.u_uPercent(gmf.result()[0])
... ).result(),
... dtOO.trimmedCurve_uBounds(
... C1, 0.0, C1.u_uPercent(gmf.result()[1])
... ).result(),
... dtOO.bSplineCurve_pointConstructOCC(
... dtOO.dtPoint3(0,0,0), C1.pointPercent(0.0)
... ).result()
... ).result()
Create an analyticSurface:
>>> aS0 = dtOO.analyticSurface(S0)
Create a gmshBoundedVolume for meshing:
>>> gBV = dtOO.gmshBoundedVolume()
Initialize the boundedVolume:
>>> gBV.jInit(
... dtOO.jsonPrimitive(
... '{'
... '"label" : "interTransMesh", '
... '"option" : ['
... '{"name":"[gmsh]General.Terminal", "value":"1."},'
... '{"name":"[gmsh]General.Verbosity", "value":"0"},'
... '{"name":"[gmsh]General.ExpertMode", "value":"1."},'
... '{"name":"[gmsh]Mesh.LcIntegrationPrecision", "value":"1.0E-04"},'
... '{"name":"[gmsh]Mesh.CharacteristicLengthMin", "value":"0.1"},'
... '{"name":"[gmsh]Mesh.CharacteristicLengthMax", "value":"0.5"},'
... '{"name":"[gmsh]Mesh.Algorithm", "value":"1"},'
... '{"name":"[gmsh]Mesh.MeshSizeExtendFromBoundary", "value":"1"},'
... '{"name":"[gmsh]Mesh.MeshSizeFromPoints", "value":"1"}'
... '],'
... '"analyticGeometry" : []'
... '}'
... ),
... None, None, None, None, None
... )
Store the underlying gmsh model in gm:
>>> gm = gBV.getModel()
Add the analyticSurface and tag the face with a string:
>>> gm.tagPhysical(
... gm.getDtGmshFaceByTag(gm.addIfFaceToGmshModel( aS0 )), "theFace"
... )
Define the B-Spline surface as transfinite face and recombine the triangles:
>>> gm.getDtGmshFaceByPhysical("theFace").meshTransfinite()
>>> gm.getDtGmshFaceByPhysical("theFace").meshRecombine()
Define all boundary curves of the face as transfinite faces and define an uniform point distribution:
>>> gm.getDtGmshEdgeByPhysical("theFace->0").meshTransfinite(1,1)
>>> gm.getDtGmshEdgeByPhysical("theFace->1").meshTransfinite(1,1)
>>> gm.getDtGmshEdgeByPhysical("theFace->2").meshTransfinite(1,1)
>>> gm.getDtGmshEdgeByPhysical("theFace->3").meshTransfinite(1,1)
Set the number of elements on the boundary edges:
>>> gm.getDtGmshEdgeByPhysical("theFace->0").setNElements(5)
>>> gm.getDtGmshEdgeByPhysical("theFace->1").setNElements(10)
>>> gm.getDtGmshEdgeByPhysical("theFace->2").setNElements(5)
>>> gm.getDtGmshEdgeByPhysical("theFace->3").setNElements(10)
Define and initialize a mesh rule with mesh operators:
>>> ob = dtOO.bVOMeshRule()
>>> ob.jInit(
... dtOO.jsonPrimitive(
... '{'
... '"_rule1D" : ["dtMeshGEdge(theFace->*)"],'
... '"_rule2D" : ["dtMeshGFace(theFace)"],'
... '"_rule3D" : [],'
... '"_only" : [],'
... '"dtMeshOperator" : ['
... '{"name" : "dtMeshGEdge","label" : "dtMeshGEdge"},'
... '{"name" : "dtMeshGFace", "label" : "dtMeshGFace"}'
... ']'
... '}'
... ),
... None, None, None, None, None, gBV
... )
Attach the observer to the gmshBoundedVolume; set thisown flag to
prevent segmentation fault:
>>> gBV.attachBVObserver(ob)
>>> ob.thisown = False
Create the mesh:
>>> gBV.makeGrid()
Create and initialize an observer to write the mesh to a msh file:
>>> ob = dtOO.bVOWriteMSH()
>>> ob.jInit(
... dtOO.jsonPrimitive(
... '{"_filename" : "interTransMesh.msh", "_saveAll" : true}'
... ),
... gBV
... )
Apply the observer to write the mesh:
>>> ob.postUpdate()
Minimization floatAtt
Import
>>> from dtOOPythonSWIG import *
Create staticPropertiesHandler and initialize:
>>> staticPropertiesHandler.getInstance().jInit(
... jsonPrimitive(
... '{'
... '"option" : ['
... '{"name" : "reparamOnFace_precision", "value" : "1.e-06"},'
... '{"name" : "reparamInVolume_precision","value" : "1.e-06"},'
... '{"name" : "invY_precision", "value" : "1.e-04"},'
... '{"name" : "xyz_resolution", "value" : "1.e-08"},'
... '{"name" : "XYZ_resolution", "value" : "1.e-07"},'
... '{"name" : "uvw_resolution", "value" : "1.e-04"},'
... '{"name" : "logLevel", "value" : "99"},'
... '{"name" : "map2dTo3d_deltaPer", "value" : "1.e-8"}'
... ']'
... '}'
... )
... )
Initialize a log file:
>>> logMe.initLog("floatAtt.log")
'floatAtt.log'
Create the function
as a vec3dMuParserTwoD-object:
>>> ff = vec3dMuParserTwoD("u,v,u*u+v*v","u","v")
Set the ranges for \(u\) and \(v\):
>>> for i in [0,1,]:
... ff.setMin(i,-100.0)
... ff.setMax(i,+100.0)
Create the infinite space \(im\) as parameter space for the function \(ff\):
>>> im = infinityMap3dTo3d()
Define an analyticGeometry as a composition of \(ff\) and \(im\):
>>> mm = vec3dTwoDInMap3dTo3d(ff,im)
Define the point \(p0\) that should be reparameterized:
>>> p0 = dtPoint3(0,0,0)
Define a pointGeometryDist object that provides the connection between the
analyticGeometry \(mm\) and the point \(p0\); pointGeometryDist
is a strategy for ``floatAtt`:
>>> att = pointGeometryDist(p0, mm)
Minimize the distance between geometry and point using a gradient-based minimization technique; the attributes of the minimizer are the strategy, the initial guess, the step size, the desired precision, and the maximum number of iterations:
>>> gradMin = gslGradMinFloatAttr(
... att,
... [0.01,.99],
... [0.001,0.001],
... 1.e-8,
... 100
... )
Convergence check:
>>> gradMin.perform()
True
Minimize the distance using a gradient-free minimization technique:
>>> min = gslMinFloatAttr(
... att,
... [0.01,.99],
... [0.001,0.001],
... 1.e-8,
... 100
... )
Convergence check:
>>> min.perform()
True
Simple Axial Runner simpleAxialRunner
Create a very simple machine that consists only of an axial runner. First an object is created by:
>>> machine = simpleAxialRunner()
The channel is created by two splines each containing two control points. Within the channel a mean plane is defined and a thickness distribution is added. The machine is created by:
>>> bundle = machine.create(alpha_2_1=40.0)
This results in a machine with an outlet angle at the shroud of 40 degree.
The OpenFOAMCase is created by:
>>> bundle.cptr_dC()["of"].runCurrentState()
The current case is then written to a directory:
>>> cDir = bundle.cptr_dC()["of"].getDirectory(
... dtOO.lVHOstateHandler().commonState()
... )
The foamlib package is used to modify the dicts.
>>> import foamlib
Initialize foamlib object
>>> fc = foamlib.FoamCase( cDir )
Before running the simulation the writeInterval and endTime is adjusted by:
>>> fc.control_dict['writeInterval'] = 25
>>> fc.control_dict['endTime'] = 50
Additionally, the flow is treated as laminar:
>>> fc.turbulence_properties["RAS"]["turbulence"] = False
The foamlib package is used to start the simulation:
>>> fc.run()
(of_...
- dtOO.test.simpleAxialRunner.simpleAxialRunner.CreateAndShow(*args, **kwargs)[source]
Create and show machine.
- Parameters:
None
- Returns:
List[ dtOO.dtBundle, dtOOInParaVIEW ] – List containing the dtBundle and the render object for ParaVIEW.
See Also
———
simpleAxialRunner.create (Create machine.)
- class dtOO.test.simpleAxialRunner.simpleAxialRunner.simpleAxialRunner[source]
Simple machine consisting of an axial runner only.
- Parameters:
None
- create(alpha_1_0: float = 90.0, alpha_1_1: float = 90.0, alpha_2_0: float = 80.0, alpha_2_1: float = 80.0) dtOOPythonSWIG.dtBundle[source]
Create machine.
The machine is created and dtOO’s logfile is created as build.log.
- Parameters:
alpha_1_0 (float, default = 90.0) – Inlet angle at hub.
alpha_1_1 (float, default = 90.0) – Inlet angle at shroud.
alpha_2_0 (float, default = 80.0) – Outlet angle at hub.
alpha_2_1 (float, default = 80.0) – Outlet angle at shroud.
- Returns:
Container that contains machine’s parts.
- Return type:
dtContainer